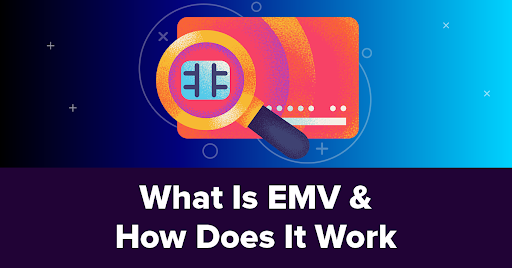
EVM Online Payment Framework
Card Detection and Reset:
The card interface functions particular to the hardware being utilized must be used to execute card detection and reset. A card will answer a reset request with an Answer To Reset (ATR), which details how the card should be interfaced with the terminal.
Candidate List Creation:
A candidate list of EMV applications that are supported by both the terminal and card must be generated by the terminal, which has a list of all the Application Identifiers (AID) of EMV apps that it is configured to support. A directory listing of all card applications may be requested by the terminal from the card’s PSE. The terminal must repeatedly ask the card whether it supports each AID in its list if this is not supported or if it cannot discover a match.
Application Selection & Read Application Data:
If there is more than one program within the finished candidate listing, or the utility requires it, then the cardholder may be asked to select software; otherwise, it can be robotically decided on.
Once the utility has been selected, the terminal provides the cardboard with any information that it requests within the PDOL and gets the processing options. The cardboard will supply the application document Locator (AFL), which is used by the terminal to study the application data from the cardboard. This information comprises the cardboard PAN and expiry date, plus many different tags of data that can be used for transaction processing which includes cardholder verification and card authentication.
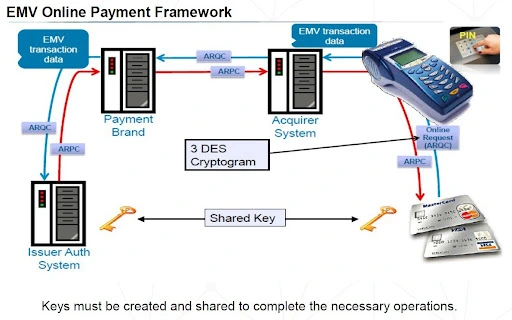
Application Cryptogram:
For the duration of an EMV chip transaction, a utility cryptogram is generated through the usage of two-key triple DES cryptography. This is a signature generated from critical data factors contained in either the web authorization request to the cardboard provider (if online authorization is needed), or the very last financial transaction required for clearing and agreement.
The cryptogram generated for the web authorization request is called the Authorization Request Cryptogram (ARQC) and the cryptogram is generated via signing statistics elements while a chip approves the payment for clearing and the agreement is called the Transaction certificates (TC). If the transaction is declined, the chip will generate a cryptogram called a utility Authentication Cryptogram (AAC).
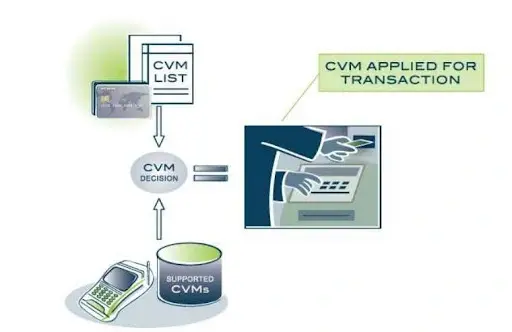
Cardholder Verification Processing:
Cardholder verification tests that the individual using the cardboard is the cardholder. The cardboard carries a Cardholder Verification approach (CVM) listing of verification methods that it supports, and the situations below which they must be carried out. The terminal must navigate through this list and attempt the primary approach it unearths for which the situation is met. If a way fails, the terminal must test whether extra methods are allowed. As an example, a listing may include an online PIN (if unattended coins), an offline PIN (if supported), signature (constantly).
Risk Management and Authorization Controls:
EMV chip transactions offer the issuing bank controls at the factor of sale which allows the issuer to lessen exposure to fraud and credit chance for offline and beneath-floor limit transactions. The issuing bank can set limits within the chip card that restrict the wide variety of consecutive offline transactions that may be processed.
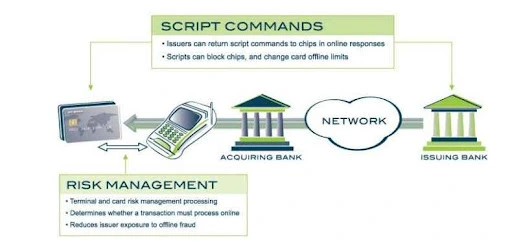
Additionally, EMV defines script instructions that can be back to the card in a web authorization reaction that lets the issuer change the cardboard limits, possibly even reducing them to 0 depending upon assessed danger profiles. Issuers may also issue scripts to block or disable a lost or stolen card.
Processing Restrictions :
Processing restrictions allow the terminal to determine the compatibility of the packages on the cardboard and terminal. This includes checking if their application version Numbers match if the card application is expired or pre-legitimate, and whether the utility usage control (AUC) allows the present-day transaction to be completed.
Terminal Action & Card Action Analysis:
The terminal will examine the results of the previous verification, authentication, and danger steps and this could bring about the terminal informing the cardboard that it proposes to both try to find online authorization of the transaction, or to complete it offline by accepting or declining the transaction locally.
During the primary Card action evaluation step, the cardboard will analyze the results of all the previous steps and this could result in the card asking for the terminal to both are trying to find online authorization of the transaction, or to complete it offline by using accepting or declining the transaction regionally. This request may also fluctuate from the motion that the terminal proposed following Terminal motion evaluation, but is a challenge to ensure common sense policies (e.G. The card isn’t always authorized to request offline acceptance of the transaction if the terminal proposed online authorization). The terminal should perform the motion that the card requested in the course of card motion evaluation.
Online Processing:
Online processing allows the card provider to research the transaction info and determine whether or not it desires to authorize or reject the transaction. This lets the company check the account’s fame and follow standards based on proper limits of threat defined by the card company, the charging scheme, and the acquirer. If no valid response is acquired from the host (e.G. Because of communications failure) then the terminal needs to perform extra Terminal action analysis to manipulate the increased stage of danger, and this could result in the terminal informing the cardboard that it proposes to both accept or decline the transaction regionally.
After online processing has been finished, the cardboard will examine the result of the net processing and will authenticate records received from the cardboard issuer. This could bring about the card asking for the terminal to finish the transaction by both accepting or declining the transaction. This request can also fluctuate from the result of online processing, however is a situation to ensure common sense regulations (e.G. The card isn’t always accredited to request recognition of the transaction if the host declined the charge).
Transaction Completed:
While the card processing has been finished, the card may be eliminated. If the transaction has been authorized then a charge may be submitted for agreement and any goods or services may be furnished.